Smoking
Smoking / Tobacco Abuse
Nicotine is the active substance in tobacco. Nicotine dependence is an addiction to tobacco products such as cigatettes, chewing tobacco, Gutka, Paan Masala etc.
Tips to stop smoking
Smoking harms almost every organ in your body including
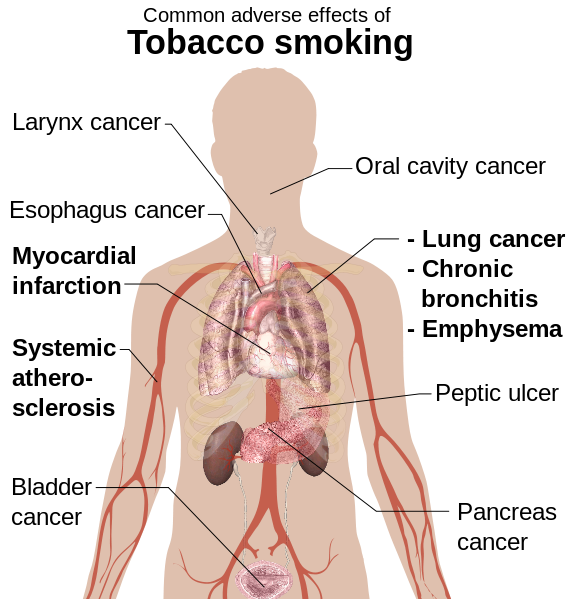
- Lung cancer and other lung diseases. Smoking is the cause of 9 out of 10 lung cancer cases, as well as other lung diseases, such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Smoking also makes asthma worse.
- Heart and circulatory system problems. Smoking increases the risk of dying of cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke. Even smoking just one to four cigarettes daily increases your risk of heart disease. If you have cardiovascular illness or heart failure, smoking worsens your condition. Stopping smoking reduces your risk of having a heart attack by 50 percent in the first year.
- Other cancers. Smoking is a major cause of cancers of the esophagus, larynx, throat (pharynx) and mouth and is also related to cancers of the bladder, pancreas, kidney and cervix, and some leukemias.
- Skin aging. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can change the structure of your skin, causing premature aging and wrinkles.
- Infertility and impotence. Smoking increases the risk of infertility in women and the chance of impotence in men.
- Pregnancy and newborn complications. Mothers who smoke while pregnant face a higher risk of miscarriage, preterm delivery, decreased birth weight and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) in their newborn.
- Diabetes. Smoking increases insulin resistance, which can set the stage for the development of type 2 diabetes. If you have diabetes, smoking can speed the progress of complications, such as kidney disease and eye problems.
- Risks to your family. Spouses and partners of smokers have a higher risk of lung cancer and heart disease, compared with people who don’t live with a smoker. If you smoke, your children will be more prone to sudden infant death syndrome, asthma, ear infections and colds.
Symptoms:
The person
- Cannot stop smoking / chewing tobacco / Gutka etc.
- Experiences physical and mood-related signs and symptoms, such as strong cravings, anxiety, irritability, restlessness, difficulty concentrating, depressed mood, frustration or anger, increased hunger, insomnia, and constipation or diarrhea, when he attempts to stop.
- Keeps smoking despite health problems. such as problems with lungs or heart.
- Gives up social or recreational activities such as going to smoke-free restaurants or socializing with certain family members or friends because he cannot smoke in these locations or situations
Treatment:
Today there are many effective treatments for nicotine dependence are available to help manage withdrawal and stop smoking for good. Many medications, including nicotine replacement therapy and non-nicotine medications, have been approved as safe and effective in treating tobacco dependence. Any of these medications, or a combination of medicines, combined with behavioral changes, can help quit smoking.
